1. Download the robocopy. It is one of the microsoft product. It stands for robust copy
This is well built GUI tool. However to understand the various options available, you can check this
http://ss64.com/nt/robocopy.html
2. Install robocopy. You can write the simple script to make the copy process. [ You can use any kind of editor like notepad, wordpad, notepad++ to write the script]
robocopy source_folder destination_folder [file(s)_to_copy] [options]
#
# Script file name: C:\mycopy.cmd
#
@echo "Copying files and folders"
robocopy "C:\myLocalFile" "F:\myBackup" /E
@echo "Copy process completed"
/E option allows to Copy Subfolders, including Empty Subfolders
3. Finally you can schedule the command file(batch file)
created by you to run in the specific time.
Go to Control Panel --> Scheduled Tasks -->
Right click and create a new schedule task -->
Give the name to it --->
Right click on the scheduled task created and go to the properties -->
specify the path of the script file in the run section under Task Tab
(in my case it would be C:\mycopy.cmd ) -->
Now go to the Schedule Tab and specify the schedule you wanted
Hey you are done.

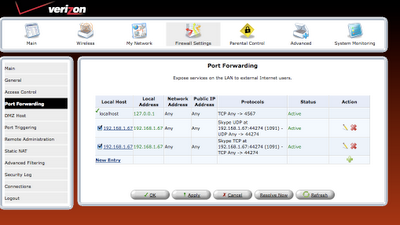
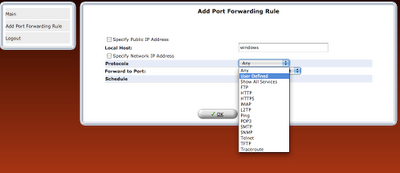
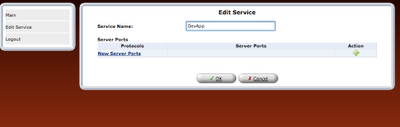
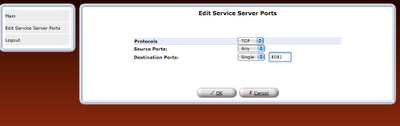
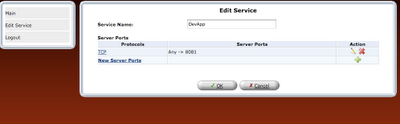
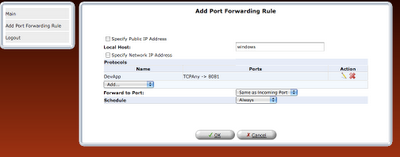
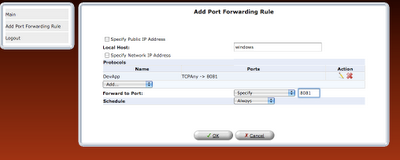

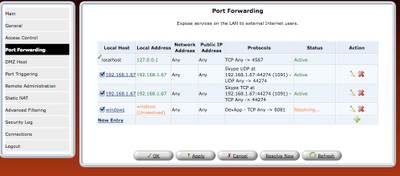
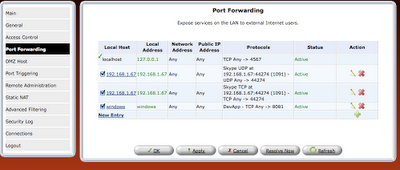
 step 8: Once the rule is defined, it should be refreshed in router or applied.
step 8: Once the rule is defined, it should be refreshed in router or applied.